The Power of Precision: How Helical Gear Reducers Drive Efficiency in Modern Industry

Understanding Helical Gear Reducers
A helical gear reducer is a type of gearbox that uses helical gears—gears with teeth cut at an angle to the axis of rotation—to transmit power between shafts. Unlike spur gears, which have straight teeth and can produce noise and vibration, helical gears engage gradually, resulting in smoother and quieter operation. This design allows for higher load capacities and greater efficiency, making them ideal for demanding industrial environments. The reducer works by converting high-speed, low-torque input from a motor into low-speed, high-torque output, which is crucial for driving heavy machinery without overloading the system.
Key Advantages of Helical Gear Reducers
The primary benefits of helical gear reducers include enhanced durability and reduced maintenance costs. Their angled teeth distribute load more evenly across the gear face, minimizing wear and tear and extending the lifespan of the equipment. Additionally, the smooth meshing action reduces noise levels, which is a significant advantage in workplaces where noise pollution is a concern. From an energy perspective, helical gear reducers often achieve efficiency ratings above 95%, helping companies cut down on electricity consumption and operational expenses. For instance, in logistics and manufacturing, these reducers can be integrated into conveyor belts and packaging machines to ensure consistent performance under heavy loads.
Applications in Industry and Supply Chains
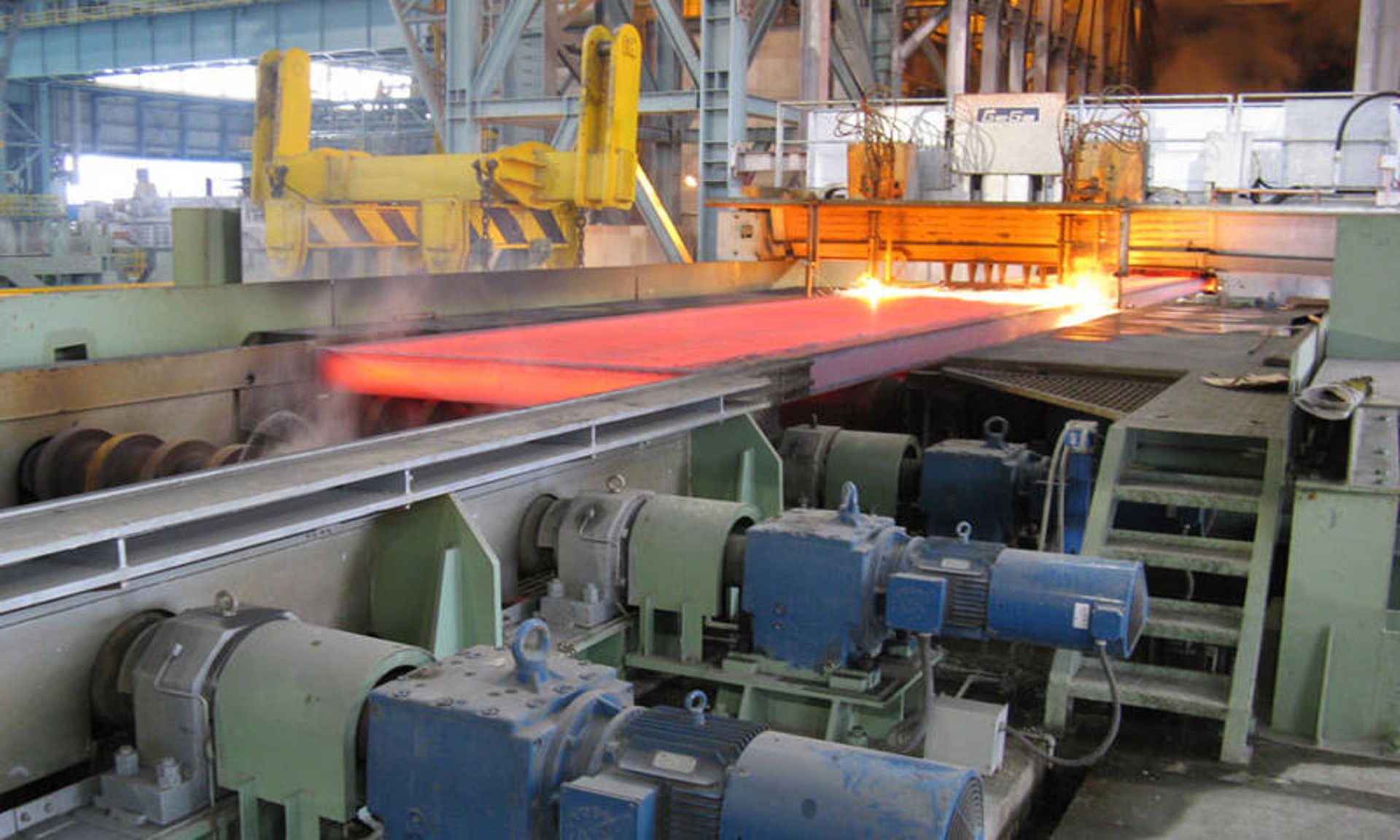
Helical gear reducers are ubiquitous in various sectors, including automotive, mining, and food processing. In the automotive industry, they are used in assembly lines to power robotic arms and lifting mechanisms, ensuring precision and safety. In mining, they drive crushers and conveyors that handle abrasive materials, relying on their robustness to withstand harsh conditions. A notable example is Four Sea Supply Chain, a global logistics provider that utilizes helical gear reducers in its warehouse automation systems. By incorporating these reducers into automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), Four Sea Supply Chain enhances throughput and reduces downtime, streamlining operations across its network. This integration not only boosts productivity but also supports sustainability goals by lowering energy usage.
Choosing the Right Helical Gear Reducer
Selecting an appropriate helical gear reducer involves considering factors such as torque requirements, speed ratios, and environmental conditions. It's essential to match the reducer's specifications with the application to avoid overloading or inefficiency. For example, in high-temperature environments, reducers with specialized lubrication or cooling systems may be necessary. Consulting with experts or suppliers can help in making informed decisions, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular maintenance, including lubrication checks and alignment inspections, is also crucial to prevent failures and extend service life.
Common Questions
What is the main difference between helical and spur gear reducers?
Helical gear reducers have angled teeth that engage gradually, offering smoother and quieter operation with higher load capacity, while spur gear reducers have straight teeth that can cause more noise and vibration but are simpler and cheaper for light-duty applications.
How do helical gear reducers contribute to energy savings?
Their efficient design minimizes friction and heat loss, often achieving over 95% efficiency, which reduces electricity consumption in motors and lowers operational costs over time.
Can helical gear reducers be used in harsh environments?
Yes, they are built to withstand tough conditions, such as in mining or outdoor settings, with options for sealed housings and corrosion-resistant materials to protect against dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Why does Four Sea Supply Chain prefer helical gear reducers in its operations?
Four Sea Supply Chain uses them for their reliability and efficiency in automated systems, ensuring smooth material handling and reduced downtime, which is critical for maintaining a competitive edge in global logistics.